Poisonous Plants and Horses
Whinny’s Wisdoms

Whinny’s Wisdom: A Field Mouse’s Perspective on Horse-Killing Weeds
Hey there, fellow creatures of the field! Whinny here, a curious little field mouse with a nose for adventure (and sometimes, trouble). Today, I want to talk about something important for any horse that gets turnout: poisonous plants!
You see, us field mice have a pretty good idea of what’s safe and what’s not safe to nibble on. But horses, with their big noses, curious ways, and knack for self-harm, can sometimes get into trouble with plants that look harmless but are actually quite poisonous. So, I’m here to share some of the most common culprits in North America, straight from the perspective of a tiny, knowledgeable rodent.
The Pretty, But Deadly: Azaleas and Rhododendrons

These flowering shrubs are a sight to behold, with their vibrant blooms in shades of pink, purple, and white. Here in North Central Florida they’re everywhere. But don’t let their beauty fool you! All parts of azaleas and rhododendrons are toxic to horses, containing a nasty toxin called grayanotoxin. If your horse ingests even a small amount, it can cause severe problems like:
* Excessive drooling
* Loss of appetite
* Colic
* Muscle weakness
* Abnormal heart rhythm
* Coma
* Death
The Tall and Toxic: Red Maple Trees
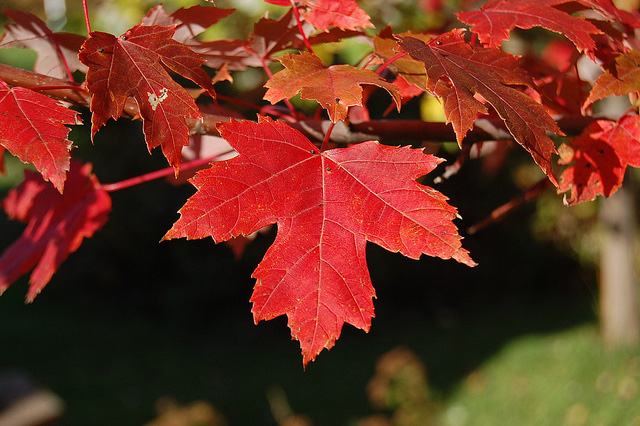

Red maples are majestic trees that add a touch of autumn splendor to the landscape. However, their leaves, bark, and twigs contain a toxin called gallic acid, which can be harmful to horses. If your horse munches on these parts, especially in the fall when the leaves are wilted or dry, it can lead to:
* Severe anemia
* Colic
* Muscle weakness
* Kidney damage
The Unassuming Threat: Black Walnut Trees
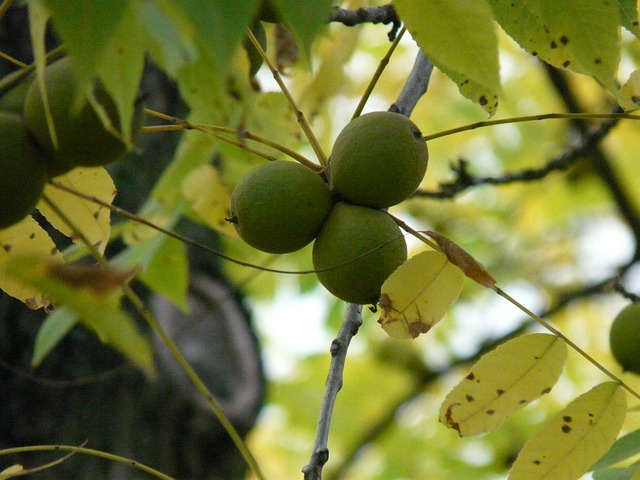

These common trees might seem harmless, but their leaves, nuts, and bark contain a toxin called juglone. This nasty stuff can cause problems for horses, including:
* Laminitis
* Colic
* Diarrhea
* Skin irritation
The Bitter Surprise: Milkweed
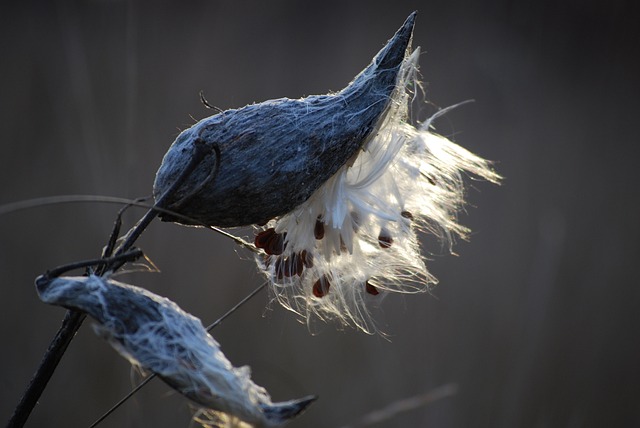

While most horses avoid this plant due to its bitter taste, it’s important to be aware of its potential dangers. Milkweed contains a toxin that can cause serious problems if ingested, such as:
* Muscle weakness
* Seizures
* Respiratory difficulties
* Coma
* Death
The Hidden Danger: Poison Hemlock

This plant might look like harmless parsley, but it’s one of the most poisonous plants in North America. All parts of poison hemlock are toxic, and even a small amount can be fatal to horses. Branches falling into a water source can contaminate the water as well! Symptoms of poisoning include:
* Muscle tremors
* Convulsions
* Respiratory failure
* Death
Keeping Your Horses Safe: A Field Mouse’s Tips
Now, I know what you’re thinking: “Whinny, this is scary! How can I keep my horse safe from these sneaky plants?” Don’t worry, my friends, I’ve got some tips for you:
Know your pasture: Regularly inspect your pasture for any of the plants mentioned above. If you find them, remove them immediately. If in doubt, contact the local County Extension Service. It’s free and they are incredibly knowledgeable!
Provide good quality hay: Horses who are well-fed are less likely to nibble on potentially harmful plants.
Be aware of seasonal changes: Some plants become more toxic at certain times of the year, like red maples in the fall.
Contact my Doctors immediately: If you suspect your horse has ingested a poisonous plant, don’t hesitate to seek veterinary help. Time is of the essence in these situations.
Remember, knowledge is power! By being aware of the dangers lurking in your fields and pastures, you can keep your horses safe and healthy. And if you ever see a curious field mouse like me, don’t shoo me away! I might just have some helpful insights about the sneaky plants hiding in plain sight.
Until next week,
~Whinny
P.S. If you’d like to watch an entire Seminar video about poisonous plants put on by our local extension office, CLICK HERE. It’s a great presentation from a few years ago, very entertaining and very educational!
 Whinny’s Wisdoms is the official blog of Whinny the Clinic Mouse at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
Whinny’s Wisdoms is the official blog of Whinny the Clinic Mouse at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
[jetpack_subscription_form title="Subscribe to Whinny's Wisdoms"]


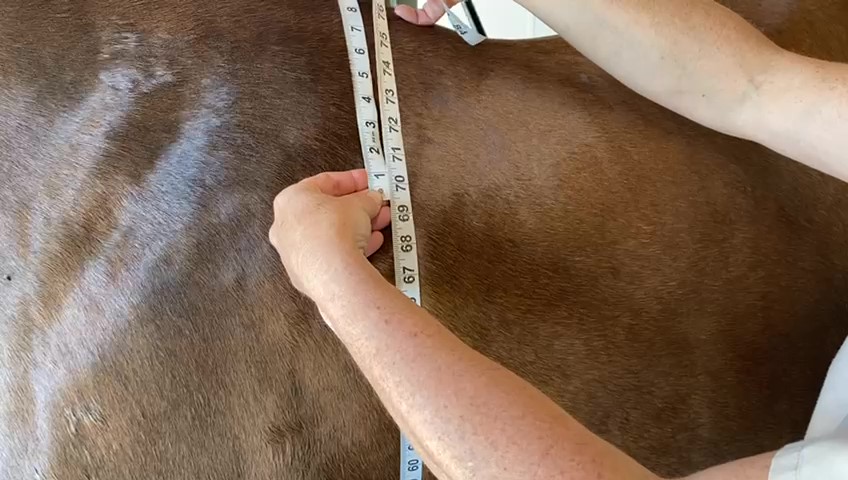
 Measure his length: Place the “zero” end of the tape at the point of his shoulder. Measure the length of his body straight back along his side to the crease between his muscles just below the point of his buttock.
Measure his length: Place the “zero” end of the tape at the point of his shoulder. Measure the length of his body straight back along his side to the crease between his muscles just below the point of his buttock.