Tuesdays with Tony
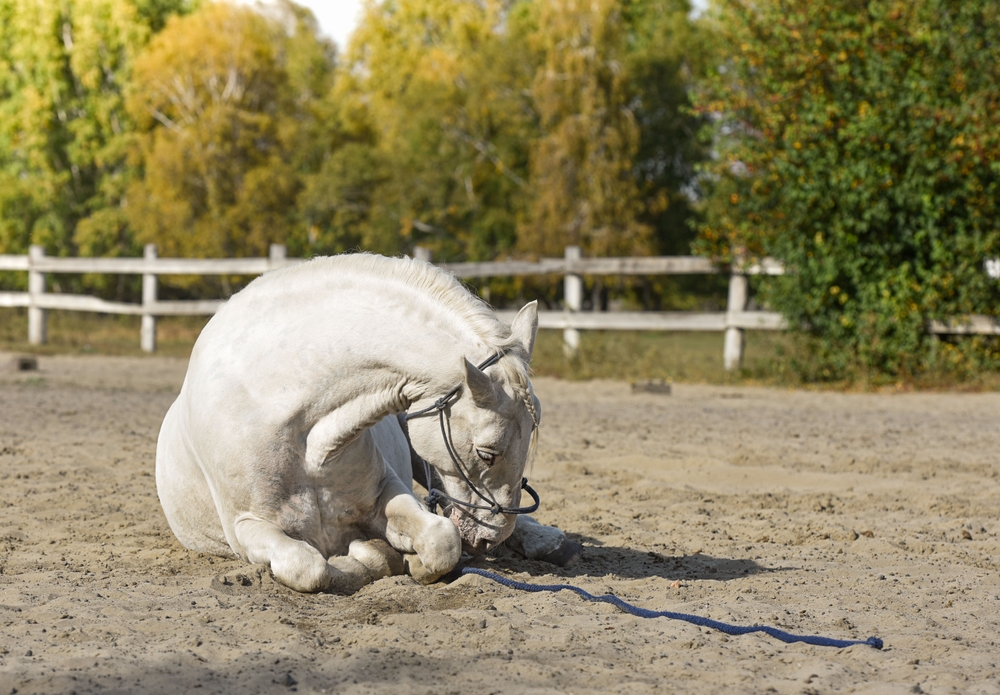
I see a lot of stuff as the Springhill Equine Clinic Cat, and it seems to me there are few things that strike more fear into the heart of a horse owner than colic. Colic is a catch-all term for abdominal pain and can be caused by a variety of different things in your horse’s belly, ranging from a mild gas colic to a serious lesion that requires surgery. I’m not sure why horses don’t just puke on the carpet (or a keyboard, I love puking on keyboards, very satisfying) like I do whenever they start to feel colicy, but my docs say that’s not how it works. Colic will never be a fun time, but here are some ways to help your horse (and my docs!) so things go as smoothly as possible.

Be Prepared
- Know how to recognize the signs of colic – Rolling, pawing, looking at the flank, and laying down are the most common signs, but horses can also show more subtle signs such as not wanting to eat, kicking at the stomach, restlessness, stretching out as if to urinate, increased respiratory rate, and reduced manure production. If you notice any of these things, give my doc a heads up so she can advise you what to do next.
- Call my doc! Even if you aren’t sure she needs to come out yet, it’s best to discuss what’s going on. If you wait too long, it could turn a mild problem into a severe one. Generally, colic is much more easily (and economically) treated if you can catch it early. A severe colic may have no chance of survival if you don’t pursue treatment immediately.
- Get yourself an inexpensive stethoscope and learn how to listen to your horse’s heart and gut sounds. You can find one for as little as $20 and my doc can show you how to use it! Practice ahead of time, don’t wait for an emergency to happen. When you call my doc, it’s very helpful to tell her what the heart rate is – it helps to determine how serious the colic is. A horse’s normal heart rate is around 26-46 beats per minute (much slower than yours, and waaay slower than my thrillingly fast kitty heartrate of 170 beats per minute) You can hear it best on the left side, just behind his elbow, about where the girth rests. A high heart rate is often a sign of a more serious colic. His gut sounds can be heard on both sides of his belly, high and low, in front of his hips. A normal horse has active rumbles all over his belly, and you shouldn’t have to listen for much longer than 15 seconds to hear some. Again, practice ahead of time to get used to his normal sounds. Keep a thermometer around, too. Practicing ahead of time will also help you keep track of what your horse’s normal temperature is, so you’ll be more likely to notice a problem. Normal temperature is usually between 98.5 – 100.5 degrees F.
- Have a transport plan. If your horse needs to get to the hospital for surgery or medical treatment, who is going to trailer him there? If you have a trailer, can it be hooked up quickly and ready to go? Are the tires and lights good? You don’t want to have to worry about these things when the colic is happening, trust me.
- Consider a major medical insurance policy for your horse. Colic surgery can be very expensive, around the mid to high 4 figures in north central Florida. Insurance can be surprisingly affordable, especially compared to the cost of treating a colic. It’s a very sad thing to have to euthanize a horse that could have been treated. When your horse is sick, the financial part is the last thing you’ll want to have to worry about. There are also colic programs from Platinum Performance and SmartPak that will cover a significant chunk of the surgery cost if your horse is enrolled.
- Be familiar with the idea of colic surgery. While hopefully you never have to use this option, you should make sure you don’t have any misconceptions about surgery. Decades and decades ago, colic surgery was less common than it is now. Some people still have the idea that colic surgery doesn’t have a great success rate. But the truth is, the survival rate for colic surgery is about 90%. Most horses can go back to athletic careers a few months after. Another misconception is that older horses can’t handle surgery well. Studies have shown that postoperative survival rates for older horses are about the same as younger horses.
While You’re Waiting for the Vet

- Give my doc good driving instructions or an accurate GPS address to find your barn. The importance of well-marked street numbers visible from the road can’t be overstated! Keep your phone close in case she needs to contact you. If the house might be hard to find, especially at night, get someone to stand by the driveway or meet at a landmark to help direct her to where your horse is.
- Have a well-lit area available for my doc to examine your horse. It should be a safe place to work and free of obstructions. Have a clean water source available in case she needs to pass a nasogastric tube into your horse’s stomach. It helps to have a power source available to plug in equipment. Also, this feline thinks you ought to put the dogs away so there are less slobbery distractions.
- Take away your horse’s food until after my doc has examined him. This includes grass, too. It’s okay to leave him water, though a colicky horse usually won’t be interested in drinking.
- Keep an eye out for manure. The amount of manure your horse has passed, and whether it’s a normal consistency, is useful info for my doc. If possible, collect some of the manure for her to inspect, as it might offer a clue about the cause of the colic. But, a common misconception is that if a horse is passing manure, the colic has to be getting better. That’s not always the case, since there are about 100 feet of gut inside your horse. The manure could be further back than the site of the problem or obstruction.
- You don’t have to continuously walk your horse, especially not for hours and hours! That can do more harm than good. A little walking (5 or 10 minutes at a time) can help to improve the activity of the intestines. But it’s okay to let him rest calmly. Laying down isn’t going to cause a twisted gut – that’s an old wives’ tale. If your horse is rolling violently and you can’t keep him up, your own safety is the priority, so it may be best to put him in a safe place and stay back until the vet arrives.
- Think about possible causes. Do you have a new batch of hay? Has your pasture changed recently? Anything else different in your horse’s lifestyle?
In Part 2, we’ll go over what will happen while my doc is examining your horse, and what to do after the vet visit, so keep an eye out for that one!
Until next week,
~Tony
P.S. Are you subscribed to my blog? Don’t rely on Facebook to let you know it’s here. Be a good human and scroll down to the purple box. You can do it, just a little more. As a reward, I’ll email you my blog every Monday, a day early!
Tuesdays with Tony is the official blog of Tony the Clinic Cat at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
[jetpack_subscription_form title="Subscribe to Whinny's Wisdoms"]