Common Colic Myths
Whinny’s Wisdoms

Hey everybody, Whinny here! Having had a horrible experience with a bad piece of cheese over the weekend, I sympathize with the horses our veterinarians see when they are having an episode of colic! As you may already know, colic is a general term for stomach pain in horses. I keep my whiskers tuned to the online horse world, and I’ve been hearing rumors and fibs that go around, making people worry even more! So, in this blog, we’re gonna tackle the top myths about colic in horses, setting the record straight and giving all you horsey lovers a clear picture of what’s what. Let’s dive in and sort out the truth from the tales!
Myth #1: Walking Helps Colicing Horses
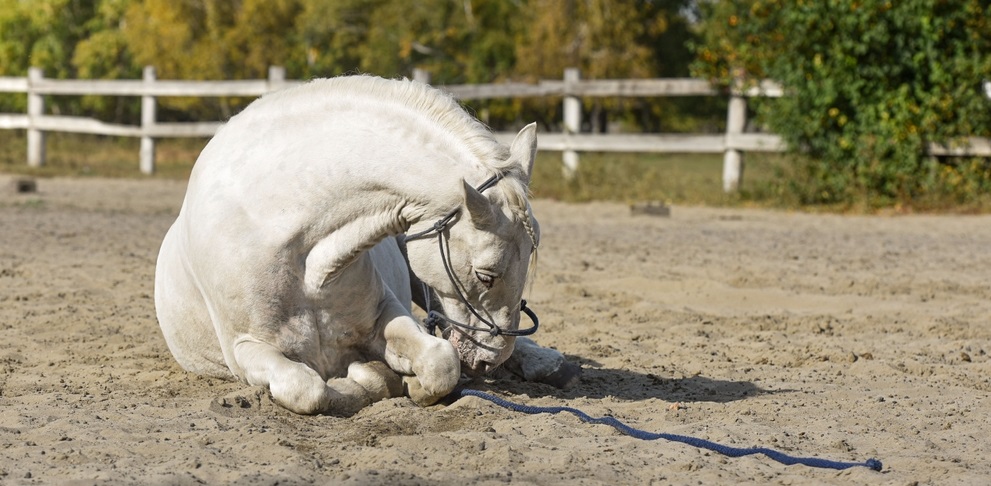
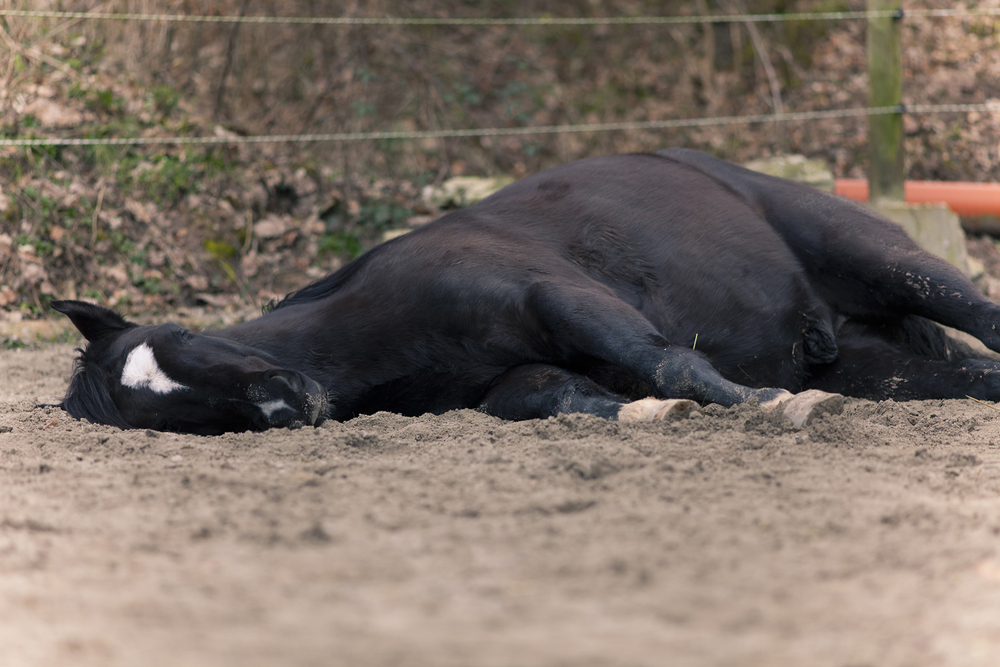
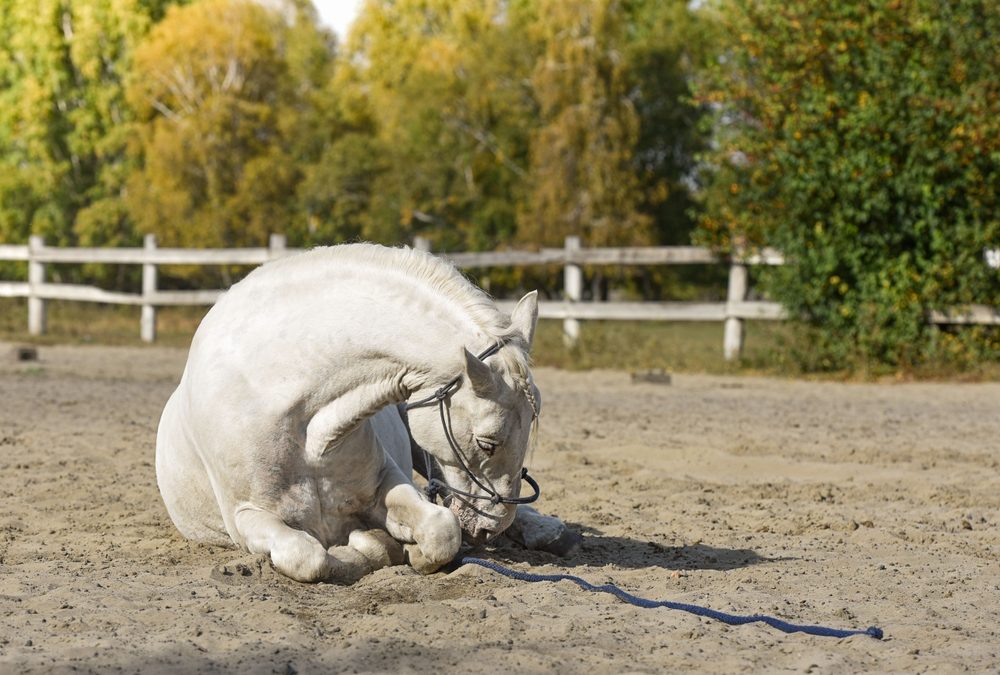
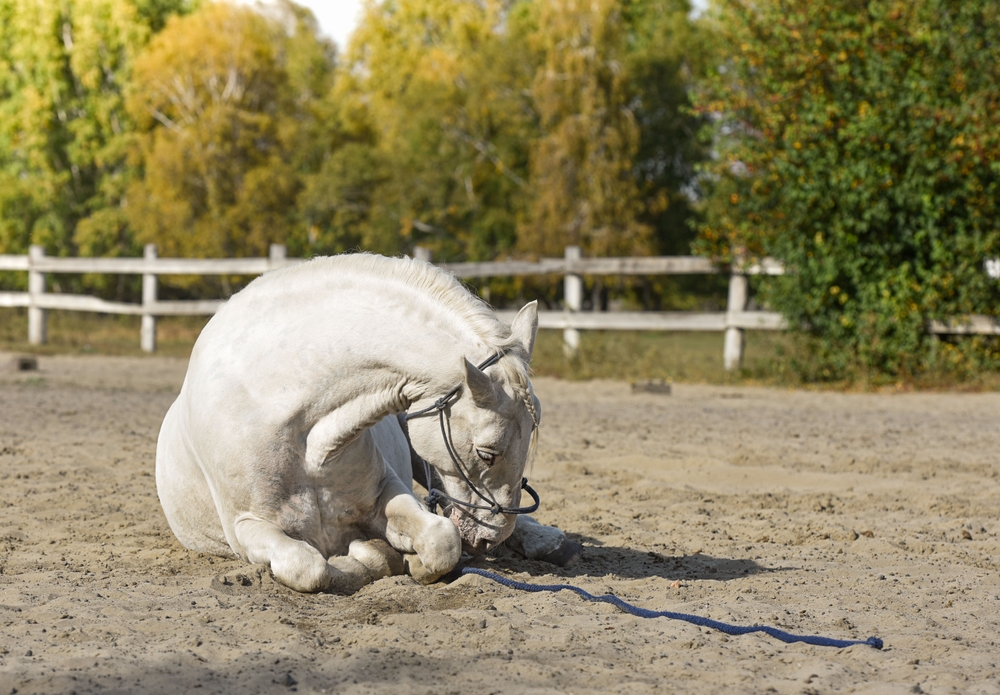
There is an old tale that has led us to believe that walking helps fix a colicing horse. Unfortunately, walking does not help and can actually make a sick horse worse by expending energy and exacerbating dehydration in hot weather. It’s okay for horses to lay down and rest while waiting for the veterinarian to arrive, even if they are rolling.
The only time my docs advise you to keep them up is when they are violently throwing themselves down or are in danger of sticking their foot through a fence or wall and injuring themselves. They always use your own experience as a rule of thumb: what do you want to do when your stomach is upset? The answer usually doesn’t involve walking a 5k! Horses need all their energy to get them through the colic episode, so don’t make them burn it unnecessarily.
Myth #2: Mineral Oil Treats Colic
Administering mineral oil orally used to be a common practice in attempting to resolve colic. However, we have since learned that administering water with a “colic salt” solution helps break down impactions and re-hydrate horses more effectively. Occasionally, we will use some mineral oil in a horse that is impacted, or constipated, as a marker of GI transit time to determine when the impaction is resolved.
My docs have a video of a great experiment that you can do at home that really makes this clear. Put one piece of horse poop in a cup of mineral oil, and another piece of poop in a cup of water. Watch what happens over the next 30 minutes. Spoiler alert: the poop in the mineral oil doesn’t do anything, while the poop in the water falls apart! And that’s what needs to happen to an impaction in your horse’s GI tract.

Myth #3: My Horse Eats Coastal And Has Never Coliced, So It’s Not An Issue For Him
Coastal hay is a lower quality and finer hay that has a higher incidence of colic. While many horses eat coastal hay without an issue, the risk is always there. To decrease the risk of colic while feeding coastal hay, we recommend feeding ¼ flake of alfalfa or peanut hay per flake of coastal hay. These types of legumes help increase gut motility, drive thirst, and generally push everything through the system with their leafy goodness.
¼ flake of alfalfa is about ¼ of a mega-calorie, so if your horse is an easy keeper, you can adjust his grain accordingly to maintain a good body condition score. If you want to learn more about calories in horse feed and hay, check out this video my docs made! It’s a great tool for helping you make adjustments to your horse’s diet without robbing them of vital nutrition.
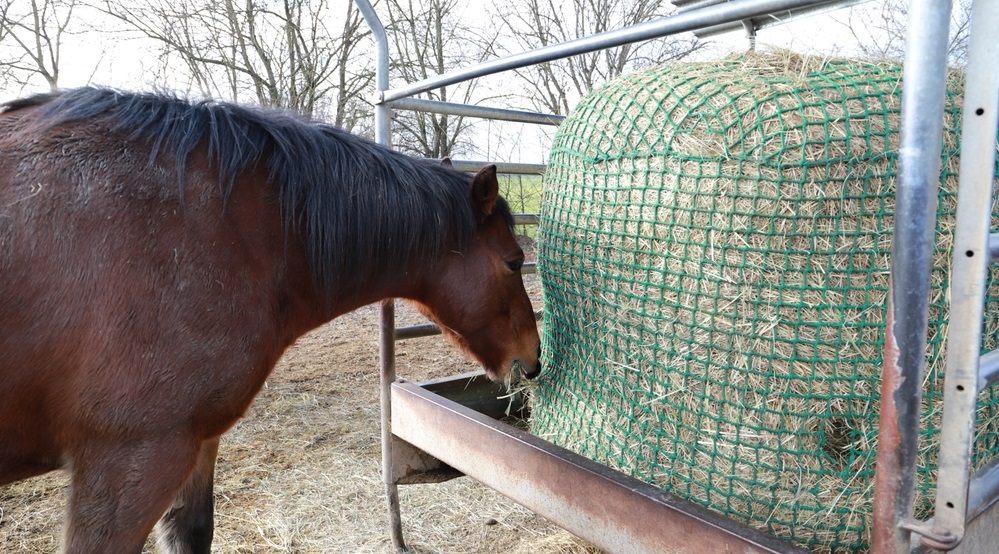
Myth #4: Horses Need to Eat 24/7
While it is true that horses are grazing animals and consistent access to forage is essential for maintaining their digestive health, overfeeding or sudden changes in diet can trigger colic.
We see this all the time when a horse overindulges on a new round bale. Moderation and gradual transitions are key!
Using slow-feed hay nets will help you stretch less hay across more time. And when transitioning from hay to grass, or vice versa, do it gradually over a few weeks to help them maintain a routine and avoid system shock. Most horses don’t do any better at self-moderating at the buffet than you people do! (I won’t discuss the eating restraint of us mice).

Myth # 5: Rolling Causes Torsion or Twisted Gut
While rolling is a sign of discomfort and colic, it does not cause the gut to twist. In a twist situation, the horse is rolling because he already has a torsion and is extremely painful from the displacement. Twists happen because the gut is spasming, like a major cramp, and has nothing to do with the orientation of the horse’s body. There are many instances of twists happening to horses who are standing quietly on the crossties or in their stalls, and are suddenly hit with high-level pain. These events are unpredictable and unpreventable, and there is no question when it’s happening.
Whinny Wisdom: If your horse suddenly freaks out and starts violently throwing himself on the ground, get out of the way and call your vet immediately! Horses in extreme pain are often focused solely on their discomfort, and may accidently injure you if you get in their space. In these situations, focus your efforts on the safety of the people and other animals in the area, and move items that the horse may injure themselves on.
Colic is a distressing condition that demands careful management and swift action. However, separating fact from fiction is crucial to ensuring the best outcomes for our equine companions. Remember, always consult with your veterinarian for professional guidance and treatment. The longer you wait to act, the harder it will be to resolve the problem, and the more it will cost. Do yourself, your horse, and your pocketbook a favor and don’t wait if your horse is showing signs of colic.
Until next week,
~Whinny
P.S. Don’t forget to check out the videos I linked above! And if you like those, our YouTube Channel is packed with great veterinary videos! Make sure you like and subscribe while you’re there 😊
 Whinny’s Wisdoms is the official blog of Whinny the Clinic Mouse at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
Whinny’s Wisdoms is the official blog of Whinny the Clinic Mouse at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
[jetpack_subscription_form title="Subscribe to Whinny's Wisdoms"]