Whinny’s Wisdoms

Hey everyone, Whinny here! More and more nowadays, horse owners are aware of how important the angles of a horse’s hoof are to his performance and the prevention of lameness. That’s a really good thing, because horses are soooo sensitive to tiny changes in the angles of their feet! If you want your horse to feel his best, compete successfully, or just stay sound for as long as possible, talking with your vet and farrier about your horse’s feet is a great place to start. You may have heard the terms “palmar or plantar angles”. These angles refer to the orientation of the coffin bone within the hoof. Palmar is the term for the front feet and plantar refers to the hind feet. Today, we’re mostly going to talk about the plantar, or hind foot angle.
What is a Negative Plantar Angle?
The planter angle is the angle the bottom of the coffin bone makes with the ground. In a healthy hind foot, we expect it to be about 2-4 degrees positive, meaning that the heel, or back end, of the coffin bone is a little higher than the toe, or front end. The exact angle depends a bit on the horse’s individual conformation. If a horse has a negative plantar angle, it means the coffin bone is “tipping up” with the front of the bone higher than the back of the bone, opposite of the way it should be. Some horses are conformationally predisposed to developing this abnormal hoof form, for example, horses with a very straight hock angles, but trimming and shoeing play a huge part in correcting or worsening the issue.
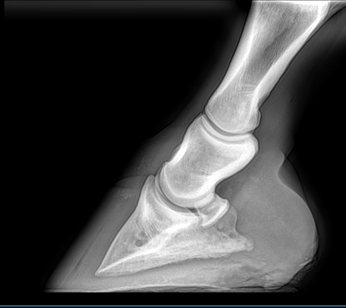
An x-ray of a normal hoof with a positive plantar angle
Why are Plantar Angles a Big Deal?
Think of it as if you had to wear shoes where the toe was wedged up higher than the heel. And you could never take those shoes off. Your back and legs would probably get sore. And what if you’re also asked to be an athlete – running, jumping, trail walking – even worse, right? You might develop some problems with your joints or lower back from your abnormal foot position and I bet your body would develop some other issues from trying to compensate. It’s the same for horses. Those negative angles put abnormal stresses on your horse’s joints and back. Scientific studies have shown negative plantar angles to be linked to pain in the gluteal muscles, proximal suspensory ligaments, stifles, hocks, and sacroiliac joints. All super important structures with a massive influence on your horse’s comfort. These issues can range from a subtle effect on performance to significant lameness.
Negative plantar angles are one of the most common hind end issues vets and farriers see. Horses that aren’t yet overtly lame may show signs like resistance during training, difficulty picking up canter leads, stumbling a little behind, dragging the hind toes, problems holding a leg up for the farrier, or lack of freedom in their hind limb swing. More severe cases can develop chronic pain and obvious lameness.
So How Can I Tell if My Horse Has Negative Plantar Angles?
Radiographs
First off, radiographs (x-rays) are the best way to know for sure. My doc will take a lateral radiograph (an image taken from the side of the horse) and measure the exact angles. This is the best way to know exactly where the coffin bone sits within the hoof capsule. She can also measure your horse’s sole depth, toe length, hoof-pastern axis, the breakover of the foot, and more. These are all really useful things to help your farrier optimize your horse’s trim. My doc can show the x-rays to your farrier, and they can come up with a trimming or shoeing plan together.
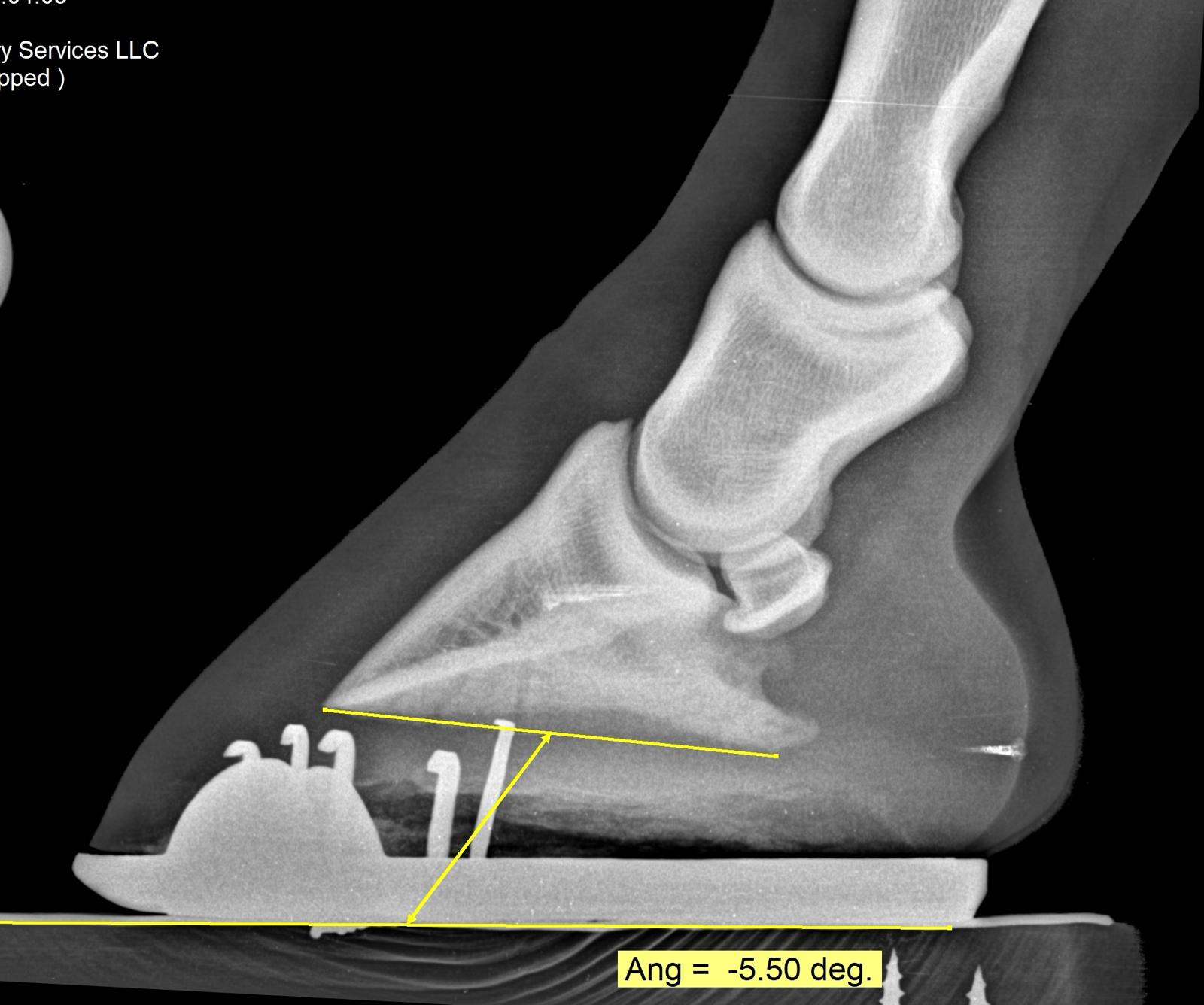
This horse has a significantly negative plantar angle of -5.5 degrees.
While radiographs are the gold standard, the rest of the strategies I’m going to list are good indicators of the problem based on external markers. They don’t give you an exact measurement or diagnosis, but they’re great tools for monitoring your horse’s feet at home.
The Shape of the Hoof
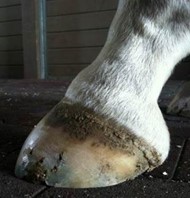
Bull-nosed appearance to the hoof.
If you pay close attention to the external shape of a horse’s hind feet, there are clues that the horse may have negative plantar angles. A bull-nosed, or bowed, appearance to the front of the hoof (the dorsal hoof wall) is typical of a severely negative angle. This is because the hoof wall follows the tip of the coffin bone, which is in essence tipping upwards and pushing outwards. Since a negative plantar angle overloads the back of the foot, the heel bulbs may also appear to be flattened.
Another sign is underneath the hoof, on his sole. In a foot with negative angles, the apex, or tip, of the frog is often deeply set in a depression in the sole. A normal hoof will have the tip of the frog positioned at about the same level as the surrounding sole, rather than sitting in a well.

A normal hoof. Notice how the apex of the frog is not deeply set in a depression.
Sometimes horses with negative plantar angles will have a squared off appearance to the hind toes, caused by dragging the feet. This can also be caused by sore hocks or other causes of lameness. Negative plantar angles can sometimes be the root cause, but not in every case. Either way, if the horse has squared off hind toes, my doc should check him out.
A steep coronary band angle is a very strong indicator of a negative plantar angle – we’ll talk about how to measure the coronary band angle shortly.
Stance
A normal horse should stand squarely, with both the front and hind cannon bones vertical, or perpendicular to the ground. When the hind hooves are out of balance, poor posture often results. Horses with negative plantar angles are frequently uncomfortable standing squarely. They may stand with their hind limbs camped under themselves, because the high toe and low heel makes it uncomfortable for them to stand with their cannon bones vertical. When the lower leg is placed vertical (as it should be in a normal horse), the hoof-pastern axis is often out of alignment, causing the horse discomfort. He will try to bring his lower limbs forward to straighten his hoof-pastern axis, but unfortunately over time this abnormal posture causes soreness in the stifles, hocks, hamstrings, and sacroiliac areas.
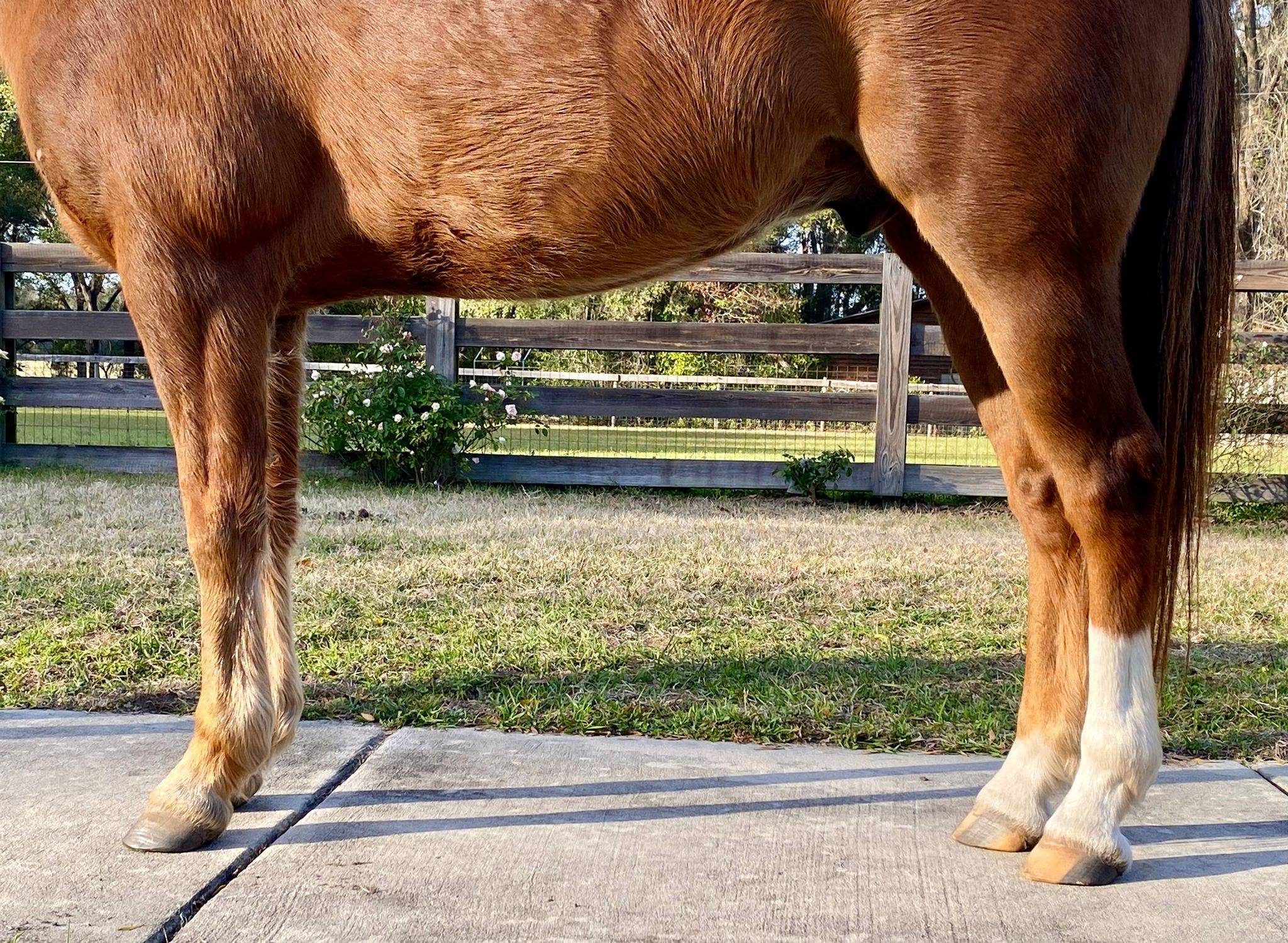
A normal, square, stance with the cannon bones perpendicular to the ground
Watch your horse to see how he tends to stand. Any horse can stand in an abnormal position for a moment, but if he consistently tends to stand with his hind limbs underneath himself, it warrants an evaluation of his feet and musculoskeletal comfort.
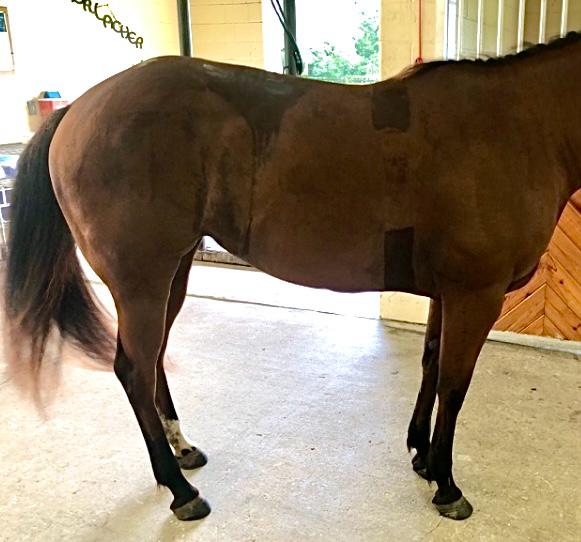
A camped-under stance
Measurements
And now for a great way for you to estimate your horse’s plantar angles at home! We’re going to look at the angle of the coronary band. A steep coronary band angle indicates low or negative angles. Remember, it’s not a substitute for x-rays, but is a good external sign of what the plantar angles are doing internally.

Stand your horse perfectly square with his cannon bones vertical
Basically, we’re going to be drawing an imaginary line through the angle of the coronary band and continuing it forward to see where it bisects the front limb. You’ll need some sort of long, thin tool – a longe whip can work, or a thin piece of wood like a long ruler or even a broom handle. If you’re handy with computers, you can also do your measurement by digitally adding a line to a photo of your horse later.
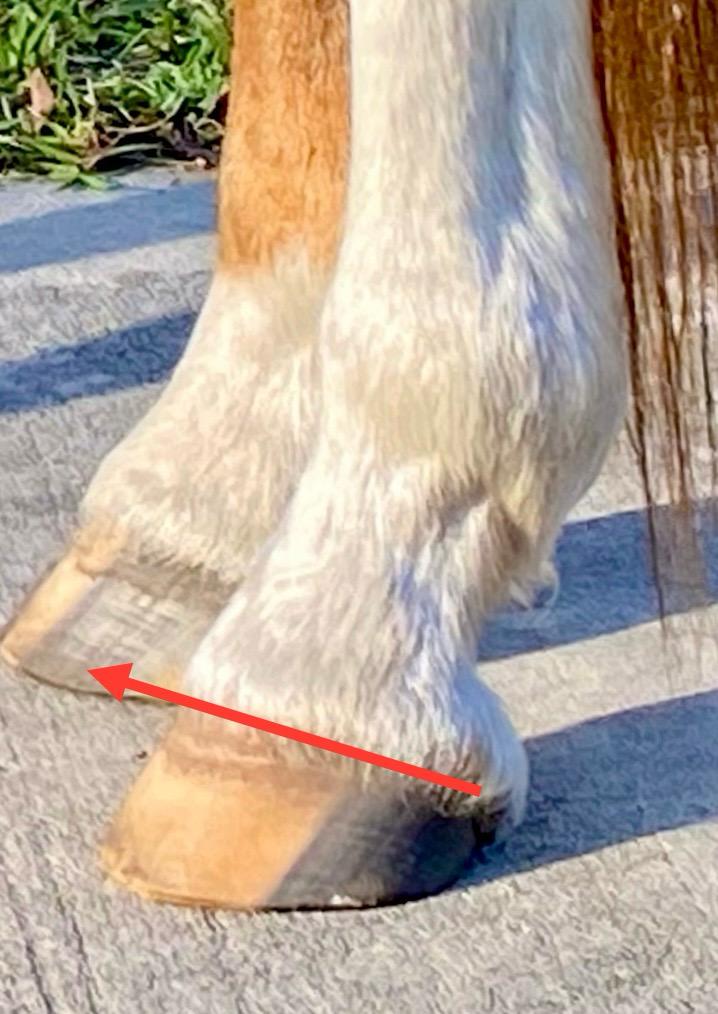

Match the angle of the coronary band
Stand your horse perfectly square with his cannon bones vertical[/caption] It’s critical that your horse stands square with his cannon bones vertical to the ground to get an accurate measurement. It may be helpful to have a set of crossties or someone to hold your horse. You’ll also want him standing on even ground. Take the tool that you’re using and line it up with the coronary band on the outside of his hoof. Raise or lower the end of your tool to match the angle to the angle of the coronary band. Now look at the forelimb on the same side – where does your tool hit that leg? In a normal horse, the line will bisect the forelimb no higher than his knee (carpus). If it’s between the knee and the elbow, there is concern that he has low or negative plantar angles. If it’s at the elbow or above, there’s a strong chance he has negative plantar angles!
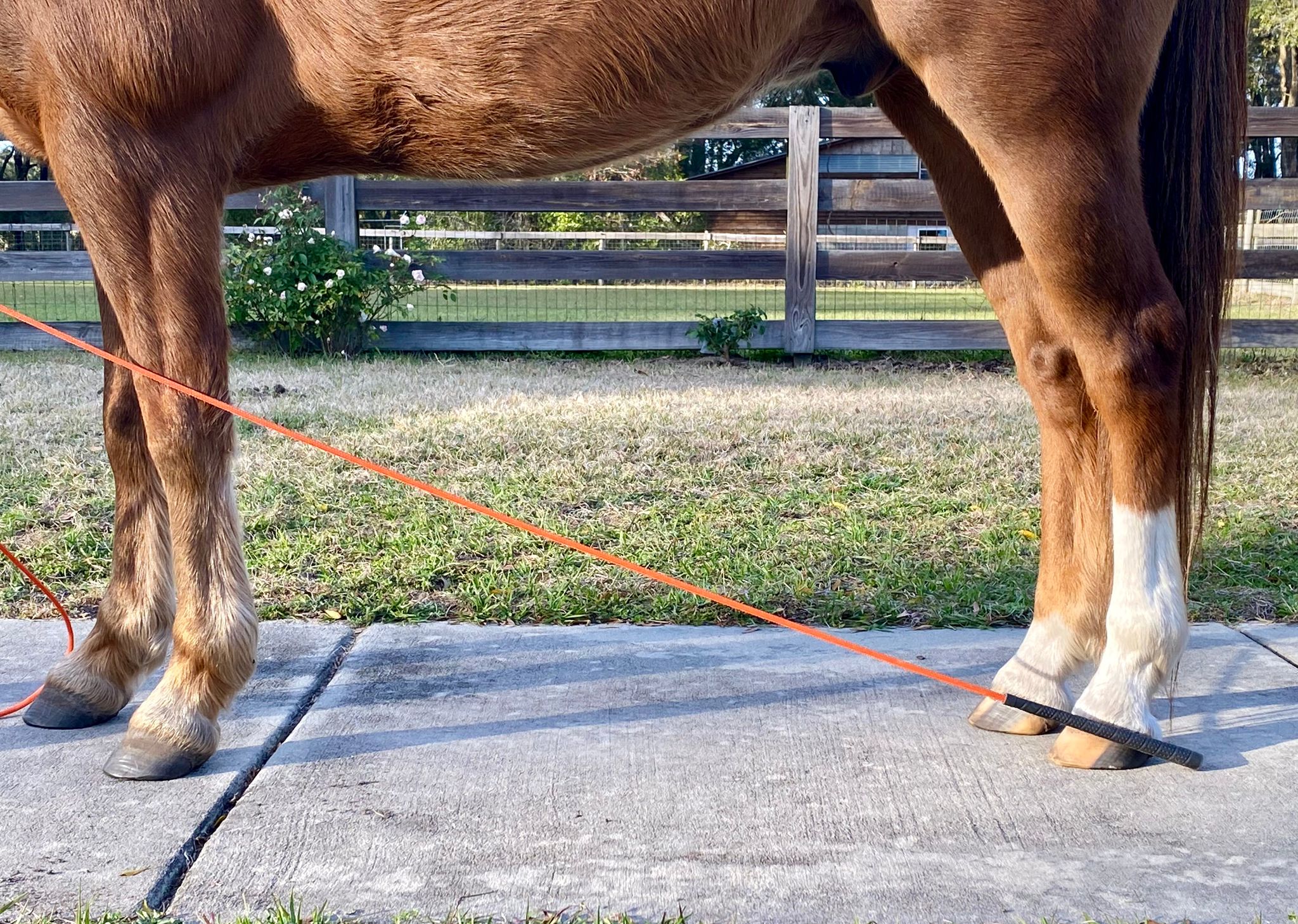
This line bisects at the level of the front knee, which is normal
These are great tools for monitoring your horse’s hoof condition at home and protecting his long-term soundness. If you have any concerns, my docs will be happy to help!
Until next week!
~Whinny
P.S. There are videos on how to check hoof angles over on my YouTube Channel. If you want to dive deeper into hoof angles, this is a great way to do it!
 Whinny’s Wisdoms is the official blog of Whinny the Clinic Mouse at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
Whinny’s Wisdoms is the official blog of Whinny the Clinic Mouse at Springhill Equine Veterinary Clinic in Newberry, Florida. If you liked this blog, please subscribe below, and share it with your friends on social media! For more information, please call us at (352) 472-1620, visit our website at SpringhillEquine.com, or follow us on Facebook!
[jetpack_subscription_form title="Subscribe to Whinny's Wisdoms"]